India has always been a land of mysteries, with a fascinating history full of surprises. From the Indus Valley civilization to the Mahabharata epic, India has a wealth of history and culture to explore.
The name “India” actually comes from the Indus River, and the Mahabharata gave us the word Bharat to describe the country. Another fascinating ancient Indian period is the Vedic period. The Vedas are a famous collection of texts that explore religion and spirituality.

Here is a list of the top 13 most fascinating facts about ancient India:
1. Introduction to the Solar System
Ancient India gave us proof of the existence of the planets and introduced the concept of the Copernican solar system based on the position of the sun. The Rig Veda indicated that the sun was in the center and the other planets orbited around it.
The concept of the sun moving on its axis also presented the idea that there is a force of attraction towards the sun as the sun was considered to be a more substantial body than the other planets.
2. Takshashila, the First University
Ancient India gave us the first ever university, Taxila or Takshashila, thought to have been established sometime between 600 BC and 500 AD in the kingdom of Gandhara. The minimum age of entry to the university was 16, and the students were taught by masters in their fields.
At one time, there were around 10,500 students who came from all over the world. The university offered 60 courses including surgery, philosophy, medicine, grammar, languages, commerce, politics, and accounting.
The university consisted of three main buildings: Ratna Sagar, Ratnodavi, and Ratnayanjak. In 1980, the university was declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
3. Ancient Discoveries
Ancient India has given the world many great inventions. The Indian mathematician Sridharacharya introduced the quadratic equation that used numbers on a much larger scale than had previously been used in Europe.
Other inventions included chess, shampoo, Indian ink, yoga, algebraic abbreviations, Pascal’s triangle, trigonometry, Ayurvedic medicine, and many more.
4. Discovery of Zero
While it is commonly believed that the ancient mathematician Aryabhata invented zero, it is probably more true to say that he was the first one to use zero as a number. It was actually Brahmagupta who coined the idea of zero.
He also introduced the idea of negative numbers and theorems that discussed cyclic quadrilateral concepts. Zero was developed as part of the decimal place value system that introduced the idea that fractions such as half or two fourths etc could be represented as exact numbers.
5. Vasco da Gama
Two people are famously credited with the search for India: Vasco da Gama and Columbus. Columbus went into the wrong direction and reached America instead, believing it to be India.
Then Vasco da Gama met a Gujarati named Kanha who helped him with navigation and became the first European to reach India by sea, thus establishing the trade routes between India, Europe, and the rest of the world.
6. Hanuman Chalisa and the Distance between Earth and Sun
In the Hindu devotional hymn, the Hanuman Chalisa, it is said that as a child, Hanumanji mistook the sun as a fruit. He decided to eat the fruit and jumped up to eat it. The deity Indra Dev offered his help to stop the sun from burning him, and it was then that the distance between the sun and earth was calculated using Hindi units of measurements.
7. Introduction to Snakes and Ladders
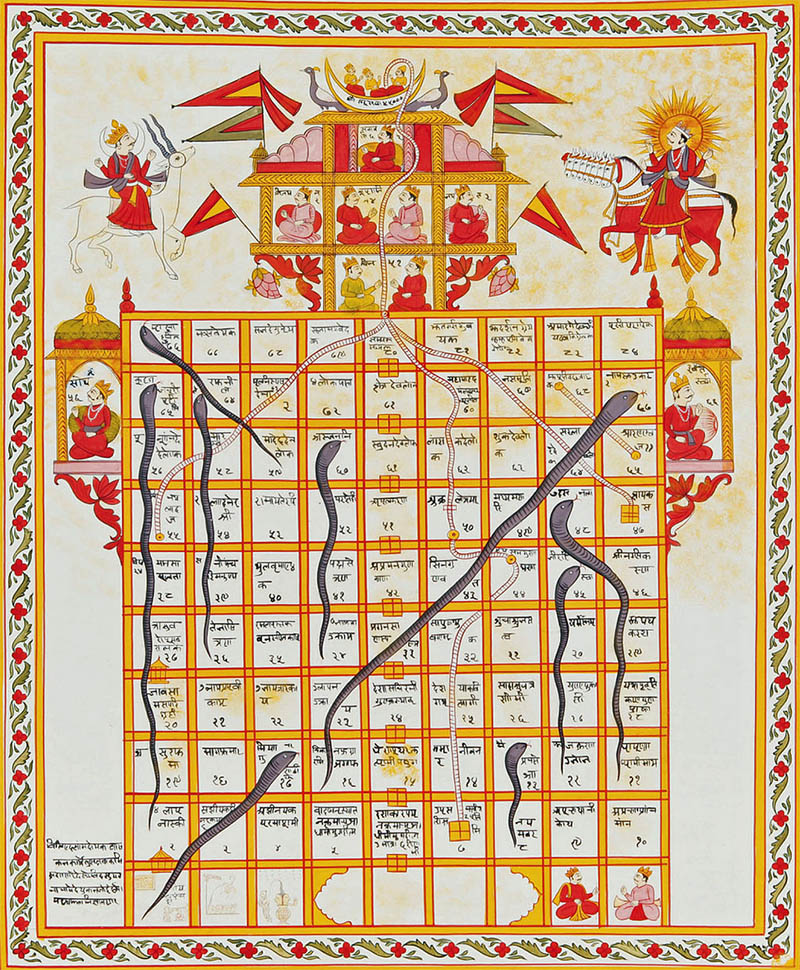
In the 13th century, a saint named Gyandev introduced the game of snake and ladders which he called mokshapatham. It came into existence for a significant reason. The snakes represented the wise men and the ladders represented good virtues.
The final destination in the game was heaven – which was attained by the ladders – but each time a snake was encountered, the player was sent down to earth to be reborn.
8. Indus Valley Civilization
When we talk about the most culture-rich, advanced civilization in history, the Indus Valley civilization springs to mind. The civilization was in what is now Pakistan and northwest India and thrived due to the rich, fertile plains of the Indus River. Evidence of religious practice in the valley can be dated back to approximately 5500 BC, while farming can be traced back to 4000 BC.
There were two major cities in the civilization: Mohenjo-Daro and Harappa. Evidence suggests that they were very advanced for the time when compared to other civilizations. For example, houses had bathrooms and proper drainage systems. The Indus civilization had a writing system which we are still not able to understand. This explains why we know so little about these ancient people.
9. Indian Vedas
The Vedas, or ancient hymns, are divided into four categories: Sama Veda, Yajur Veda, Rig Veda, and Atharva Veda. These were considered to be a spiritual encyclopedia for Indians, offering knowledge on many different subjects.
The Rig Veda spoke about the hymns that were recited, the Sama Veda talked about the melodies that should be chanted, the Yajur Veda contained sacrificial formulas, and the Atharva Veda taught the magical methods.
The Rig Veda, being the largest of them all, was divided into ten books that were then called Mandalas. The Yajur Veda was divided into two categories that explained how to perform religious rituals and sacrifices.
10. Games in India
India was the birthplace of chess which originated in north India in the sixth century, after which it spread to Persia. However, chess is not the only game which was invented in India. Kabaddi, kho-kho, polo, cards, and snakes and ladders (see 7) also began in India.
Most of these games were invented for the ancient Indian kings, and when we look back at Hindu scripture, we can see that often the marriages of princes were decided by a game. For example, in the Mahabharata, Arjun married Draupadi after hitting a fish eye with an arrow.
11. Jewelry in India
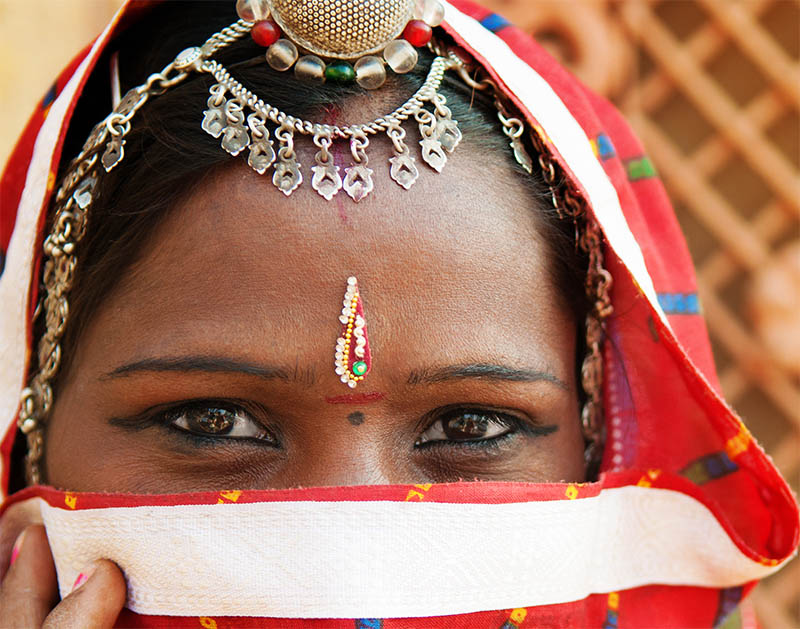

Jewelry has always been an integral part of Indian culture, and can be seen in images of Indian goddesses or read about in Indian scriptures. Gold and diamond jewelry is still important for Indian women.
According to the Gemological Institute of America, India was the only source of diamonds in the world up until 1896. The famous diamond on Queen Elizabeth’s crown, the Kohinoor, was found in India. The Nizam of Hyderabad also gave Queen Elizabeth II a beautiful diamond necklace as a wedding present.
12. Indian Emperors
Many great emperors contributed to the history of India such as the famous Chandragupta Maurya who founded the Mauryan Empire and was responsible for Indian unification. Another great emperor was Ashoka.
He was considered to be one of the greatest emperors of India and ruled the Maurya dynasty. He was said to be an aggressive king and was known as Ashoka the Fierce. Another famous emperor was Samudragupta, also known as “India’s Napoleon,” who was leader of the Gupta dynasty from 335 to 375 AD.
Another famous king was Raja Raja of the Chola dynasty. However, perhaps the most famous of them all was the Mughal emperor Akbar who was a strong and influential leader.
Conclusion
Whether it is in the fields of education or science, ancient India has given the world many great inventions and discoveries. Ancient India has also provided the world with a rich cultural heritage through its traditions and ancient texts and scriptures, many of which are still read and practiced today.